Introduction
As the global community continues to grapple with the urgent need to address climate change, businesses are increasingly becoming aware of their environmental impact. One crucial aspect of corporate sustainability is measuring and managing greenhouse gas emissions. Scope 1 emissions, in particular, play a significant role in understanding and reducing an organization’s carbon footprint.
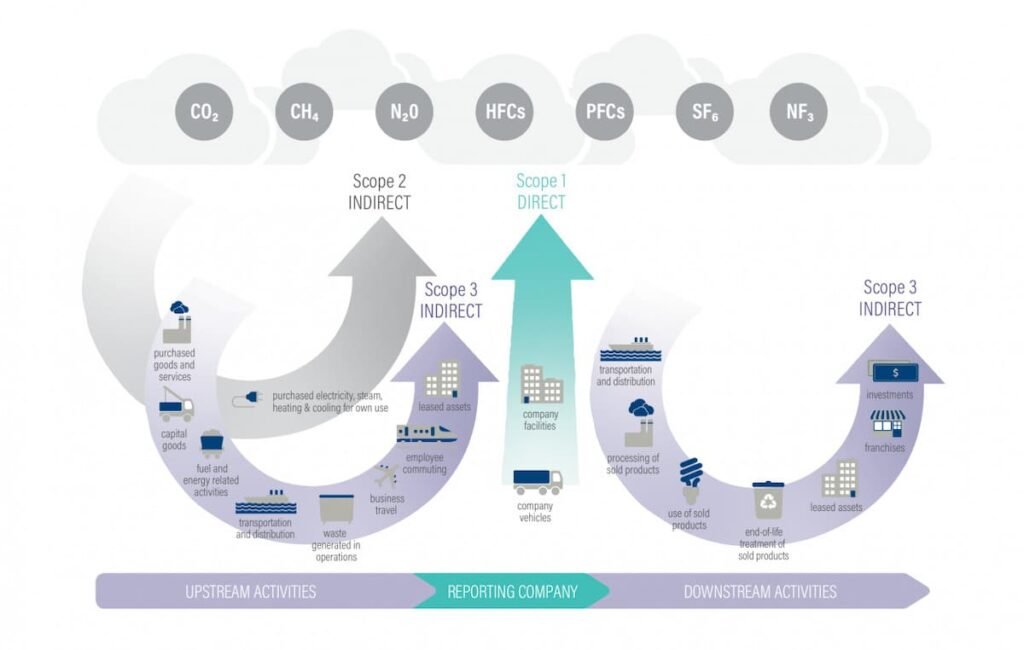
What are Scope 1 Emissions?
Scope 1 emissions refer to direct greenhouse gas emissions that occur from sources owned or controlled by a company. These emissions are typically generated from on-site facilities, such as manufacturing plants, office buildings, or company-owned vehicles. Examples of Scope 1 emissions include combustion of fossil fuels, such as natural gas or diesel, for heating, power generation, or transportation.
Why are Scope 1 Emissions Important?
Understanding and managing Scope 1 emissions is crucial for several reasons:
- Carbon Footprint: Scope 1 emissions contribute directly to a company’s carbon footprint. By measuring and reducing these emissions, organizations can take significant steps towards mitigating their overall environmental impact.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many countries and regions have implemented regulations and reporting requirements for greenhouse gas emissions. By monitoring and managing Scope 1 emissions, companies can ensure compliance with these regulations and avoid penalties.
- Reputation and Stakeholder Expectations: Increasingly, consumers, investors, and other stakeholders expect companies to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. Managing Scope 1 emissions can enhance a company’s reputation and help build trust with stakeholders.
Measuring and Managing Scope 1 Emissions
Accurate measurement and reporting of Scope 1 emissions are essential for effective management. Here are some key steps involved:
- Identify Emission Sources: Companies need to identify and categorize all their sources of direct emissions. This includes assessing fuel consumption, energy use, and other relevant activities.
- Collect Data: Accurate data collection is crucial for calculating emissions. This involves gathering information on fuel consumption, energy usage, and other relevant parameters from various sources within the organization.
- Calculate Emissions: Once the data is collected, emissions can be calculated using established methodologies and emission factors provided by recognized bodies such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
- Set Reduction Targets: Based on the emissions data, organizations can set ambitious reduction targets to align with their sustainability goals. These targets can drive initiatives towards adopting cleaner energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and implementing sustainable practices.
- Implement Mitigation Strategies: To effectively reduce Scope 1 emissions, companies can implement various strategies such as investing in renewable energy, adopting electric vehicles, improving energy management systems, and optimizing production processes.
Conclusion
Scope 1 emissions are a critical component of corporate sustainability efforts. By understanding and managing these direct emissions, organizations can take meaningful steps towards reducing their carbon footprint and contributing to global efforts to combat climate change. It is crucial for businesses to prioritize the measurement, reporting, and reduction of Scope 1 emissions to ensure a sustainable future for our planet.
More Information: circulartree.com